I have setup my Lab in a docker container using the ubuntu 20.04 image from docker hub.
I have downloaded the md5collgen tool and set it up. Since I couldn’t get a way to install the bless editor in the container, I have decided to use xxd to get the hex dump data from the binary file.
Lab Tasks
3.1 Generating Two Different Files with the Same MD5 Hash
Question 1: If the length of your prefix file is not multiple of 64, what is going to happen?
Answer:
Prefix Size = 48 bytes
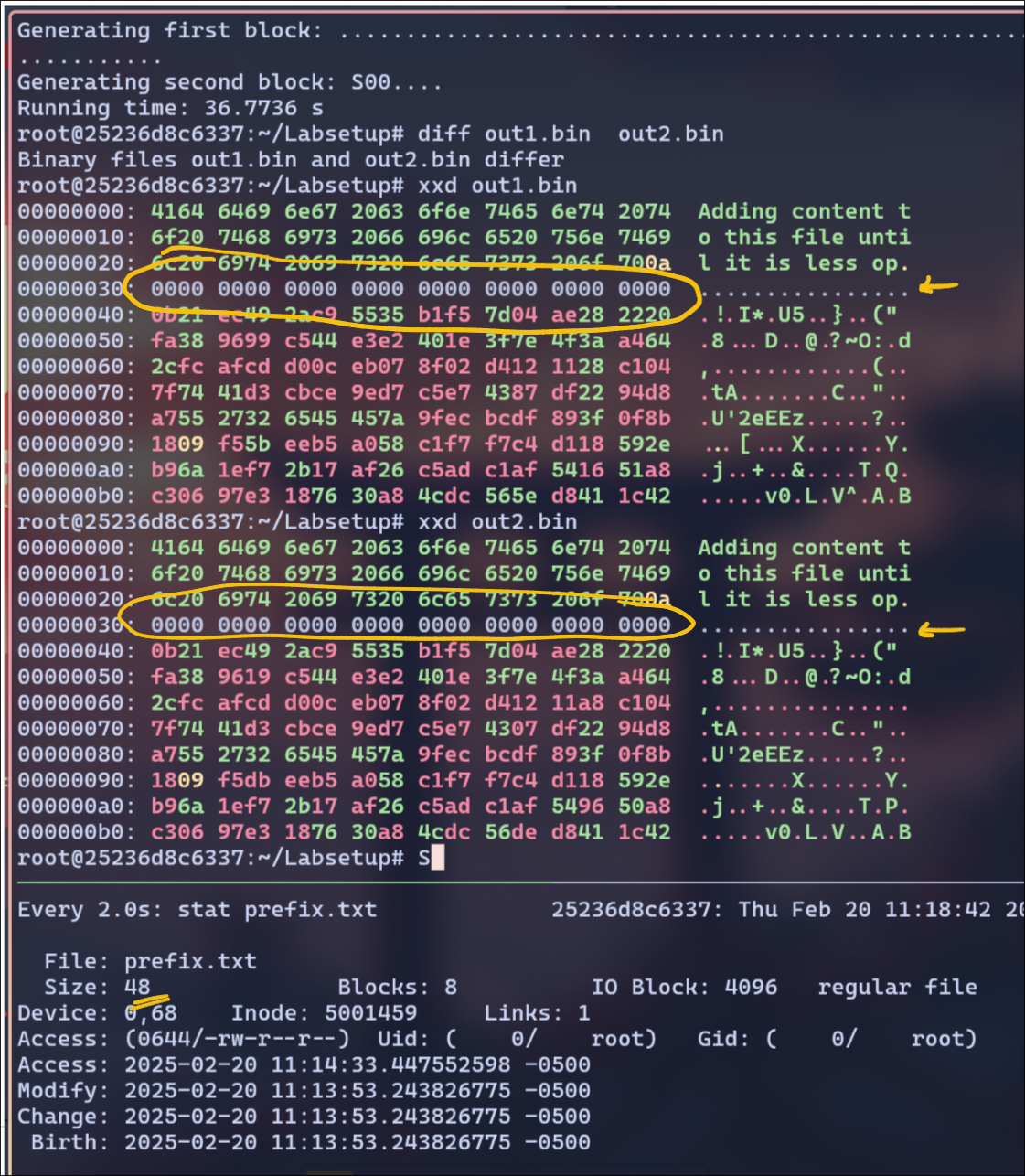
Here, my prefix is less than 64 bytes(not multiple), I see the out1.bin and out2.bin files are mismatching. The m5collgen tool adds padding to the prefix to make it 64 bytes to ensure the input is properly formatted.
- 16 bytes of padding were added. The padding bytes are just Zeroes
- The padding could add unintended differences in the output files, which might affect the collision.
-
This is why the generated binary files were not perfectly identical in structure.
Question 2. Create a prefix file with exactly 64 bytes, and run the collision tool again, and see what happens.
Answer:
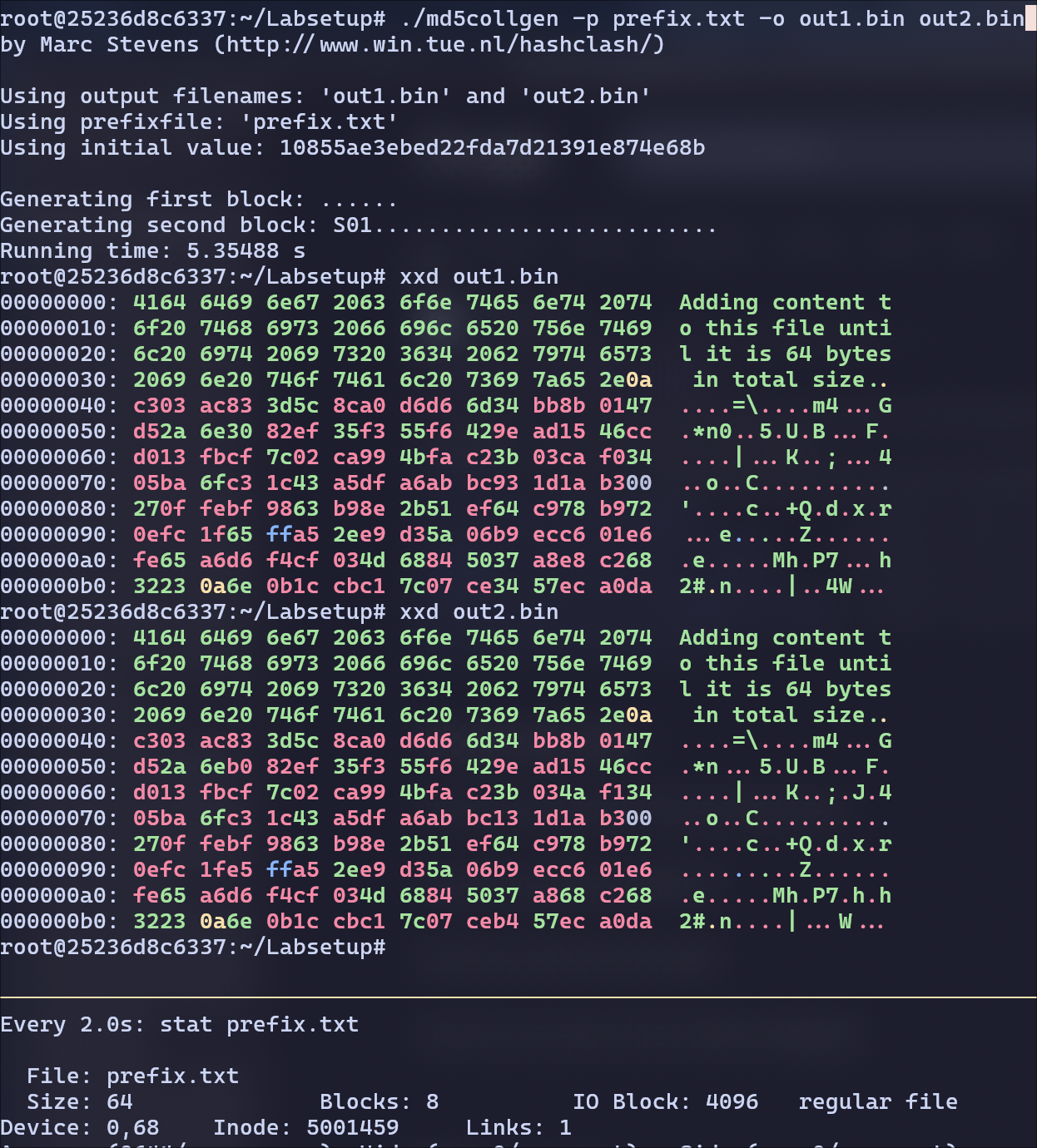 Since the prefix file is now 64 bytes, the tool didn’t need to add any padding. All it did is, it added
Since the prefix file is now 64 bytes, the tool didn’t need to add any padding. All it did is, it added P to out1.bin and Q to out2.bin.
Question 3. Are the data (128 bytes) generated by md5collgen completely different for the two output files? Please identify all the bytes that are different.
Answer:
The 128 bytes generated by md5collgen are completely different for both the cases. Whether the prefix is padded to get 64 bytes or not, the P and Q are different but they do have some similarities.
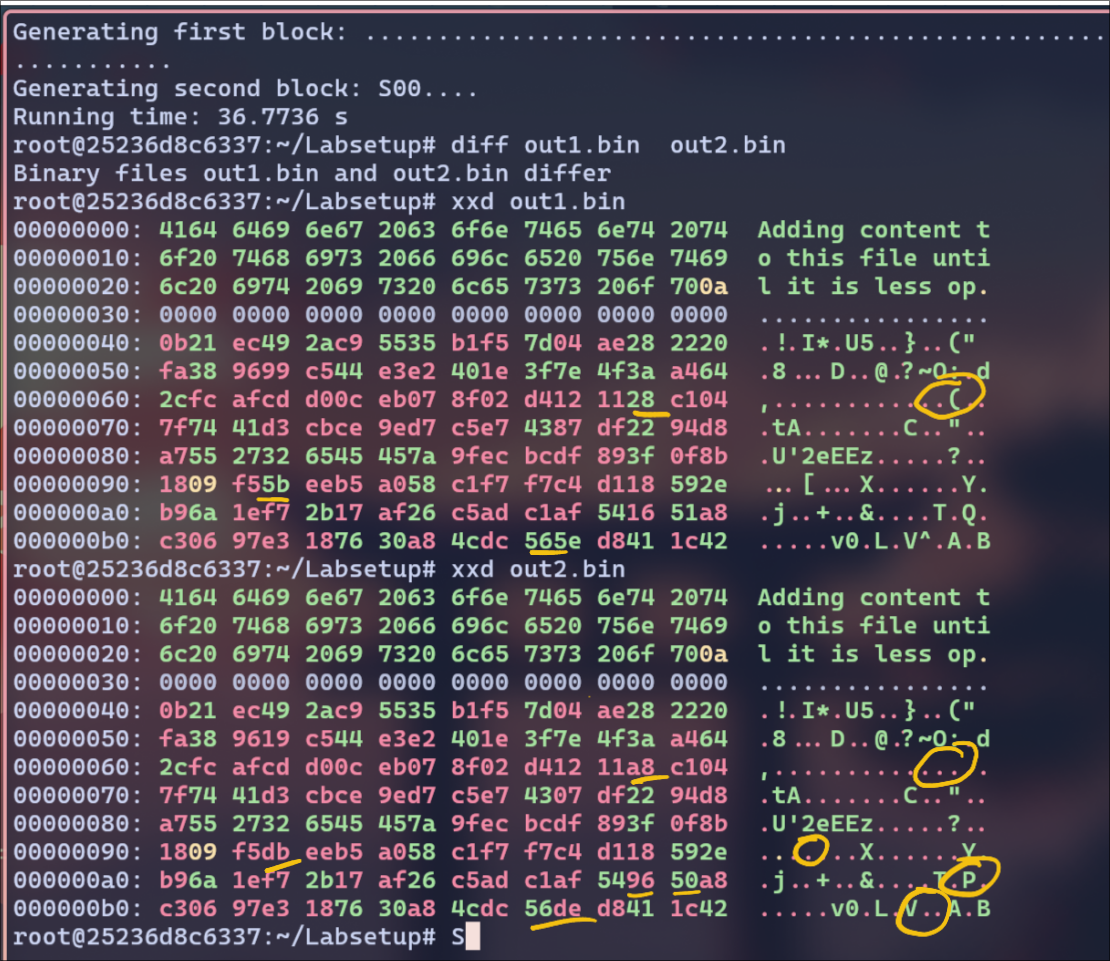
here are the differences b/w out1.bin and out2.bin
With padding file:
Without Padding:
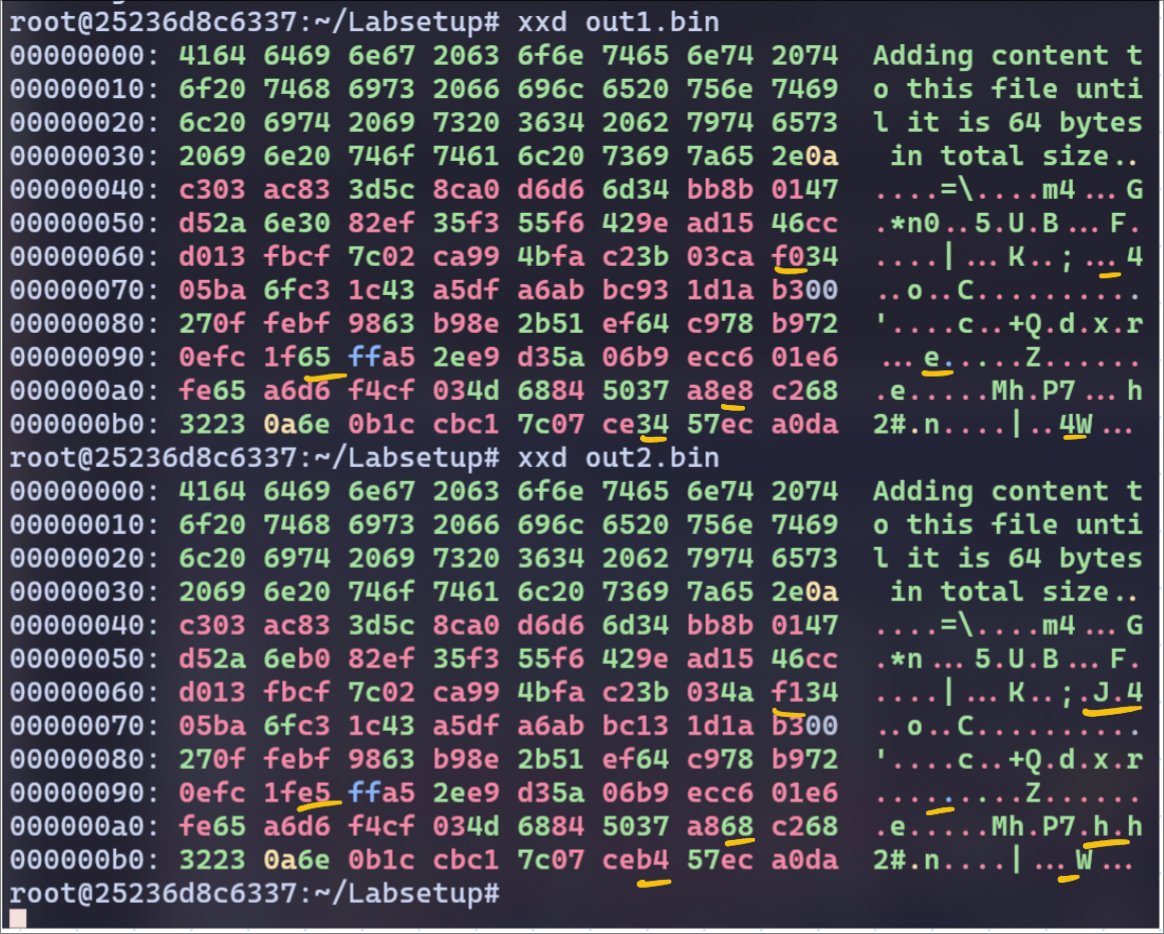
I can see a pattern here. The P and Q even though they are random strings, they are almost same. Only bytes 47, 84, 110, 124 differ from out1.bin and out2.bin.
3.2 Task 2: Understanding MD5’s Property
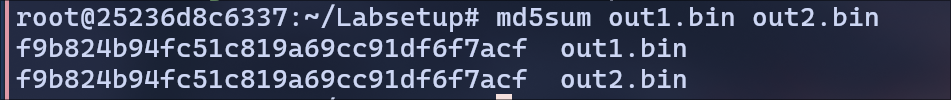
For out1.bin and out2.bin, I ran the md5sum command and the below is the output:
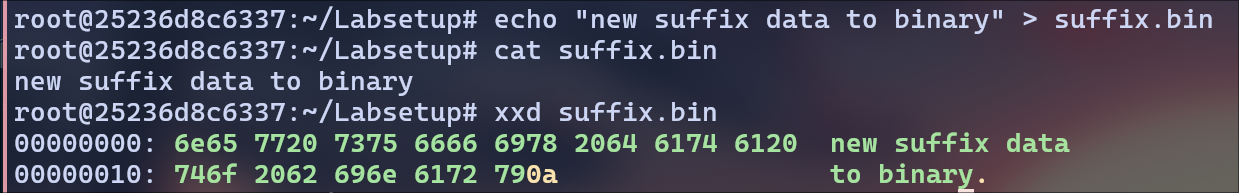
Created a new suffix file called suffix.bin:
I have concatenated the out1.bin with suffix.bin file and the same for out2.bin file.
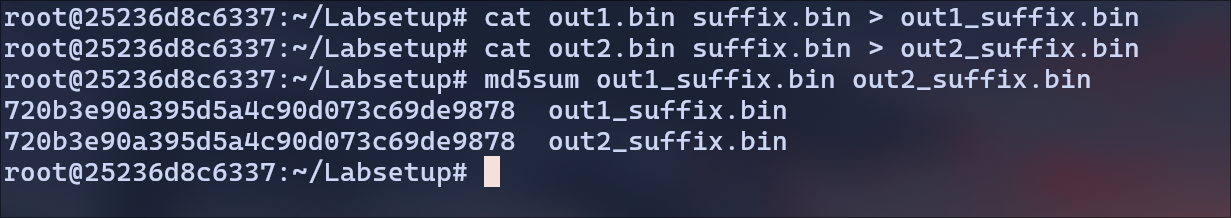
MD5(out1.bin) = MD5(out2.bin) and MD5(out1.bin I suffix.bin) = MD5(out2.bin I suffix.bin)
where I represents concatenation.
3.3 Task 3: Generating Two Executable Files with the Same MD5 Hash
MyCode:
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned char xyz[200] = {
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
};
int main() {
int i;
for (i=0; i<200; i++){
printf("%x", xyz[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
Compile it:
gcc code.c
Check the hex output using xxd
xxd ./a.out
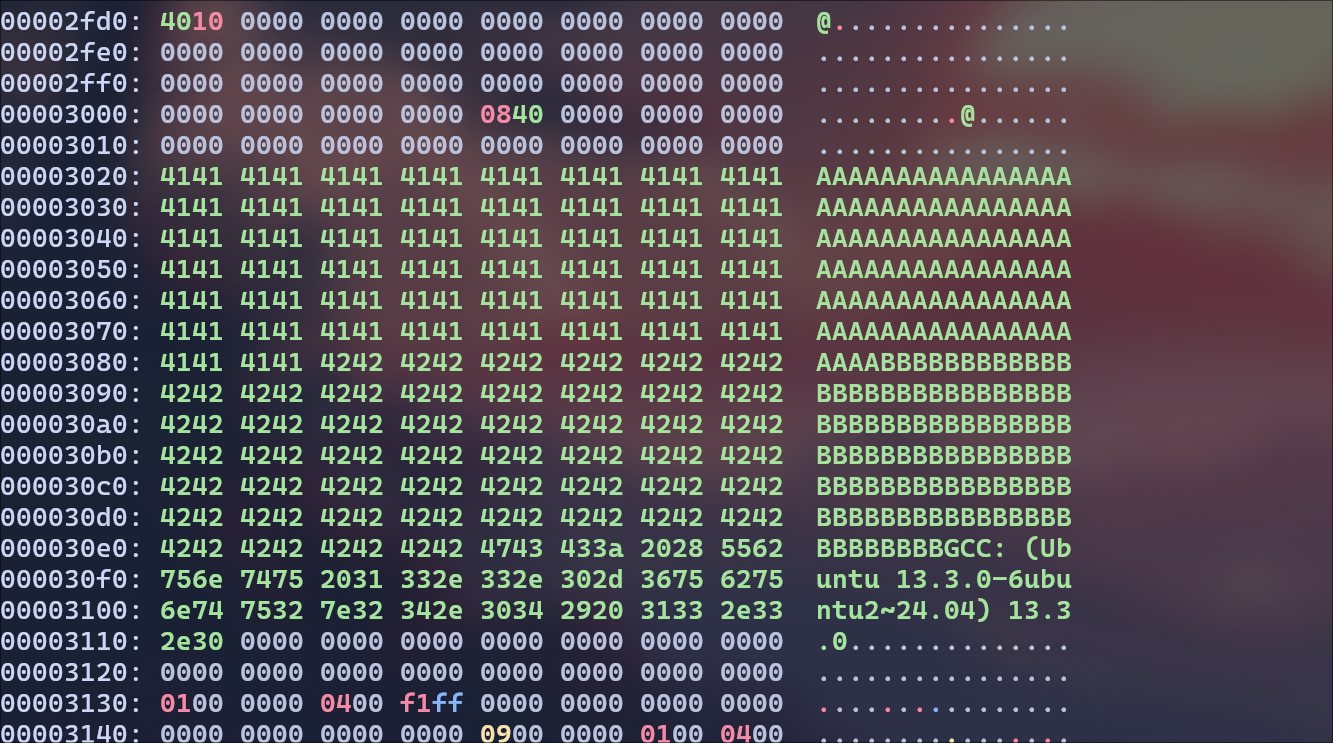
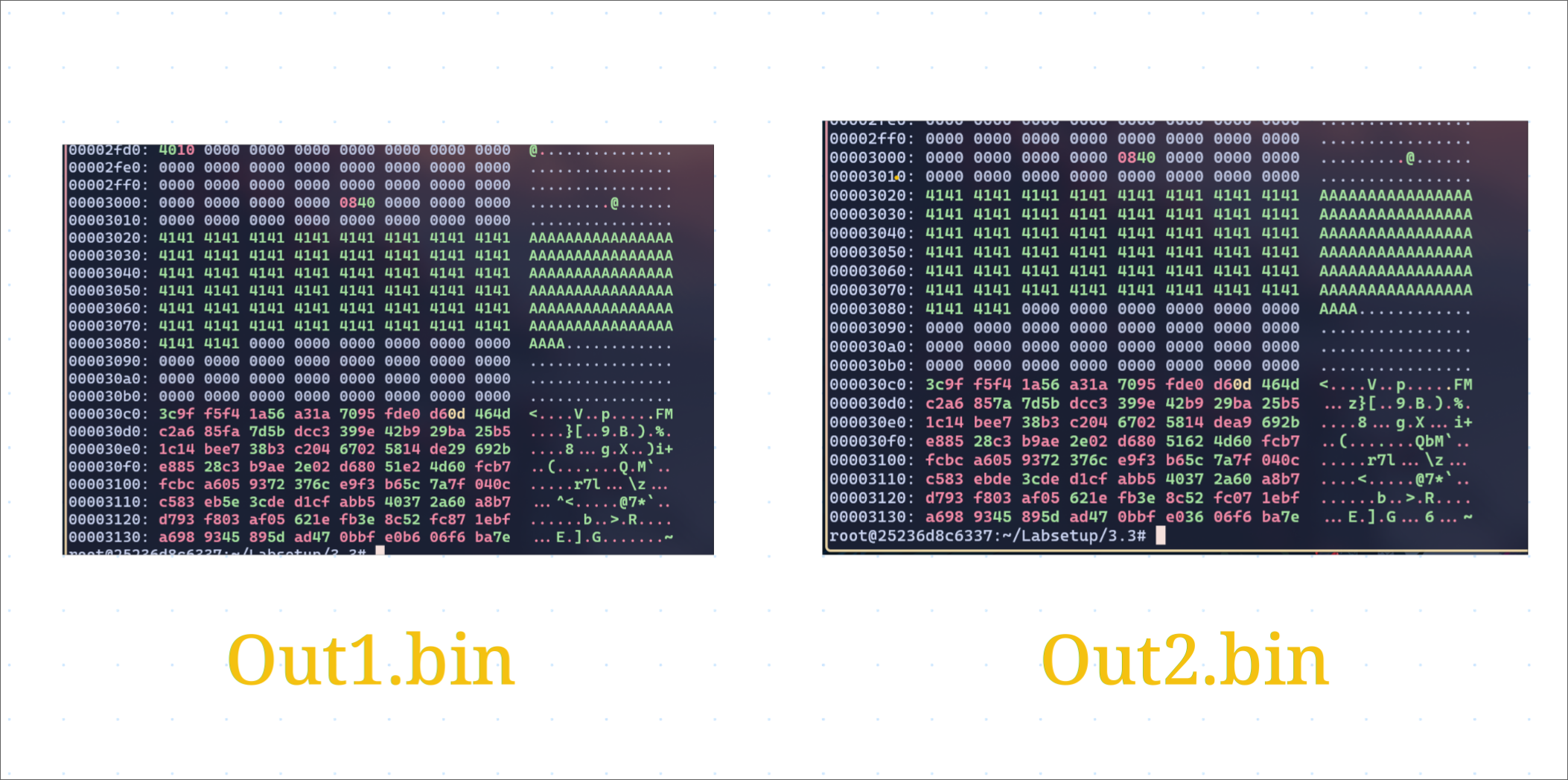
Now, the letters A start at 3020, but I wanted to split it at half of the char array(at 3084 or 12420 in decimal) so I get all A’s in the prefix.
head -c 12420 a.out > prefix
Generating the out1.bin and out2.bin
./md5collgen -p prefix -o out1.bin out2.bin
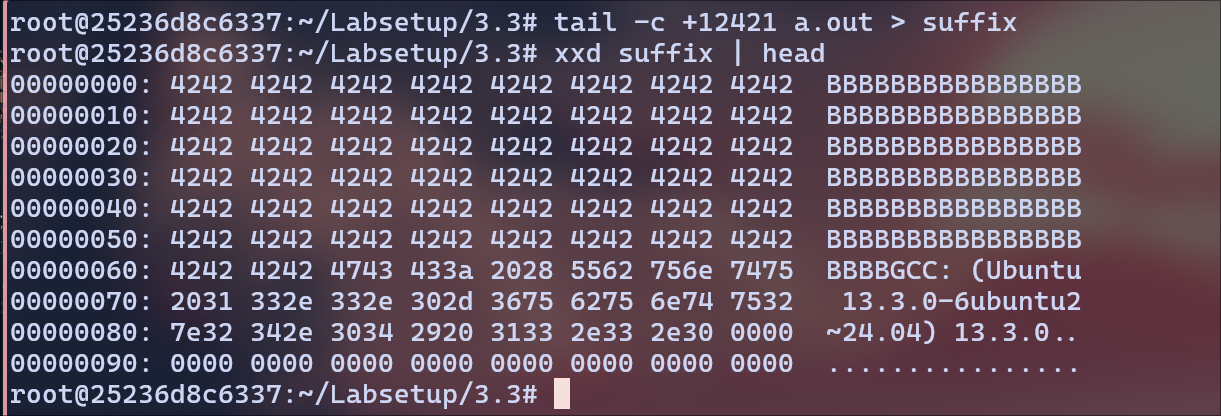
Adding the remaining text to suffix (from hex 3085 or 12421)
tail -c +12421 a.out > suffix
Add the suffix to out1 and out2 to create to files using cat command.
Also provide the executable permissions and check the output of the files and their md5sum.
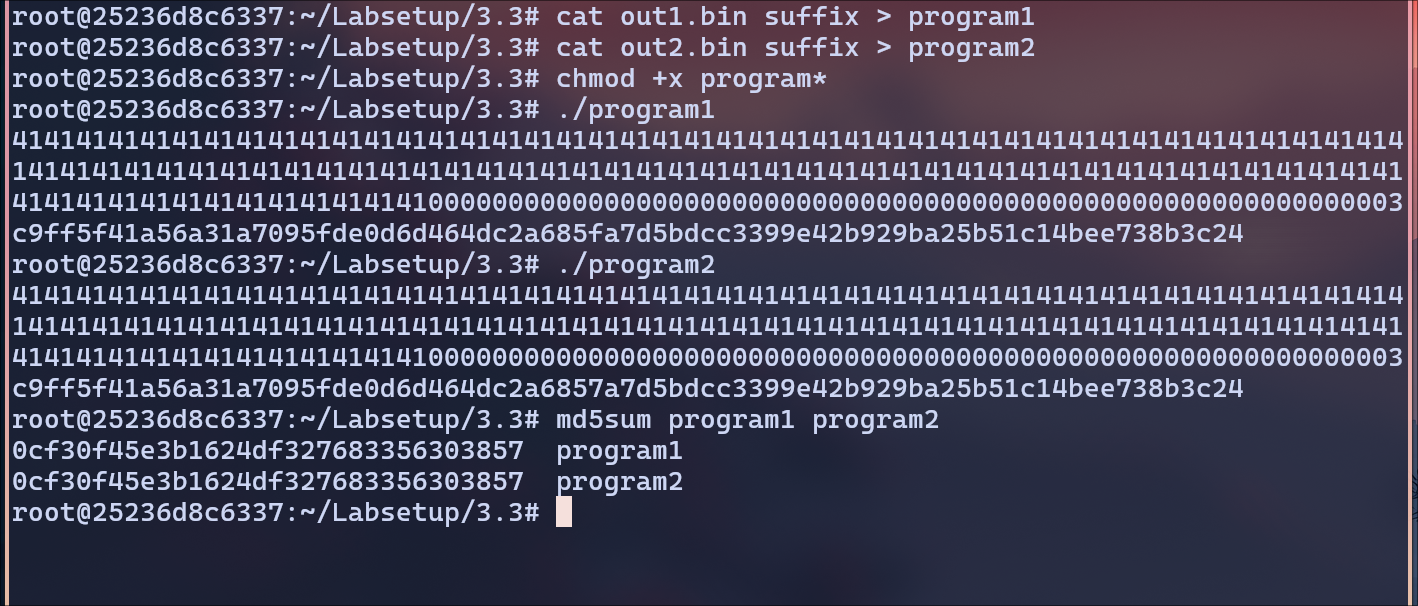
The hashes match and we get the same output for both program1 and program2 files.
3.4 Task 4: Making the Two Programs Behave Differently
The below code is used for creating two programs that behave differently.
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned char Arr_A[200] = {
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
};
unsigned char Arr_B[200] = {
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41, 0x41,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42,
};
int main() {
int i;
int foundMatch = 0;
for (i=0; i<200; i++){
if(Arr_A[i] == Arr_B[i]) {
foundMatch = 1;
} else {
foundMatch = 0;
break;
}
}
if(foundMatch){
printf("Running Safe Code! and this is the intended behaviour\n");
} else {
printf("OOOH! Running some --MALICIOUS-- code..\n");
}
}
compile the code:
gcc code.c

We can observe the hex values for first array starting at 3020 and so I will extract the data before this to prefix.
head -c 12420 a.out > prefix
Using md5collgencommand to create 2 binary files with the same hash
./md5collgen -p prefix -o P_prefix Q_prefix
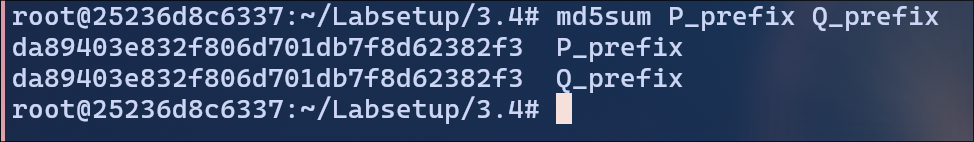
Now, we need to connect the prefix files to correct suffix files.
Upon on observation of the prefix files, there is 188 bytes of difference b/w P_prefix and prefix file and the same for Q_prefix.
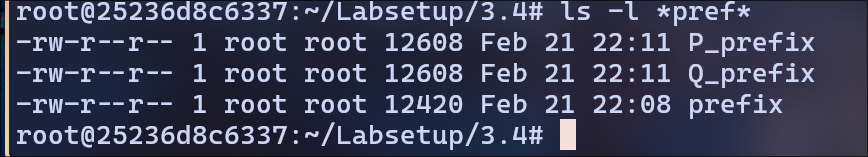
So, the suffix file is everything after the first 12421 bytes from the a.out file.
Create suffix: Skip 128 bytes for P or Q
tail -c +12609 a.out > suffix
To get P file, we know 148 bytes are generated extra by md5collgen
tail -c 128 P_prefix > P
tail -c 128 Q_prefix > Q
checking suffix:
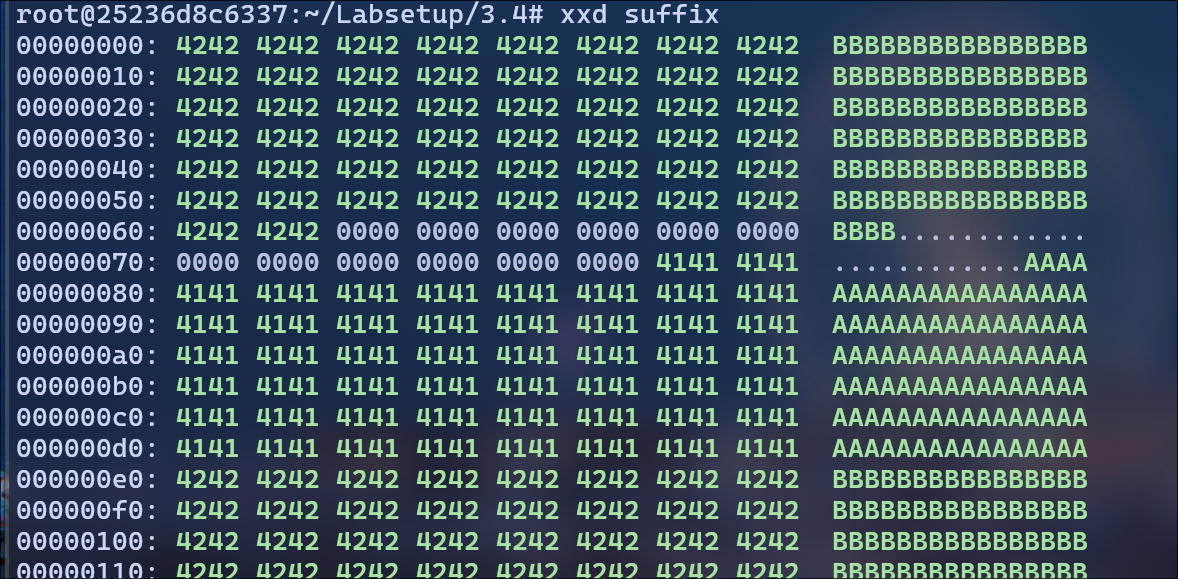 Now, we observe second array starts at 00. I’m adding extra 100 bytes to get middle of second array at e0.
Now, we observe second array starts at 00. I’m adding extra 100 bytes to get middle of second array at e0.
head -c 32 suffix > middle
So, everything after middle file will be our commonsuffix file. Since P is 128 bytes and middle is about 64 bytes, the commonsuffix file would be everything in the suffix file after 362 (128+32) bytes.
tail -c +161 suffix > commonsuffix
At final, we will concatenate everything together:
cat P_prefix middle P commonsuffix > benignCode
cat Q_prefix middle Q commonsuffix > maliciousCode
chmod +x benignCode maliciousCode
Verifying MD5 Hash:
md5sum program1 program2
We have same hash.
Running the programs and checking their behavior.
Program1: